-
-

BRUSHING & FLOSSING
How to BrushWhat Is the Right Way to Brush?
Proper brushing takes at least two minutes — that's right, 120 seconds!...

BRUSHING & FLOSSING
How To FlossWhat is the Right Way to Floss?
Proper flossing removes plaque and food particles in places where a toothbrush cannot easily reach... -
Science & Innovation
- Home
- Oral Health
- What Are The Stages Of Gum Disease?
What is gum disease?
Gum disease is an inflammation of the gums that can progress to affect the bone that surrounds and supports your teeth. It is caused by the bacteria in plaque, a sticky, colourless film that constantly forms on your teeth. If not removed through daily brushing and flossing, plaque can build up. The bacteria infect not only your gums and teeth, but eventually the gum tissue and bone that support the teeth. This can cause them to become loose, fall out, or they may have to be removed by a dentist.
There are three stages of gum disease:
- Gingivitis: This is the earliest stage of gum disease, an inflammation of the gums caused by plaque build-up at the gumline. If daily brushing and flossing do not remove the plaque, it produces toxins (poisons) that can irritate the gum tissue, causing gingivitis. You may notice some bleeding during brushing and flossing. At this early stage in gum disease, damage can be reversed, since the bone and connective tissue that hold the teeth in place are not yet affected.
- Periodontitis: At this stage, the supporting bone and fibres that hold your teeth in place are irreversibly damaged. Your gums may begin to form a pocket below the gumline, which traps food and plaque. Proper dental treatment and improved home care can usually help prevent further damage.
- Advanced Periodontitis: In this final stage of gum disease, the fibres and bone supporting your teeth are destroyed, which can cause your teeth to shift or loosen. This can affect your bite, and if aggressive treatment cannot save them, teeth may need to be removed.
How do I know if I have gum disease?
Gum disease can occur at any age, but it is most common among adults. If detected in its early stages, gum disease can be reversed, see your dentist if you notice any of the following symptoms:
- Gums that are red, puffy or swollen
- Gums that bleed during brushing or flossing
- Teeth that look longer because your gums have receded
- Gums that have separated, or pulled away, from your teeth, creating a pocket
- Changes in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
- Pus coming from between your teeth and gums
- Constant bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth.
How is gum disease treated?
- The early stages of gum disease can often be reversed with proper brushing and flossing. Good oral health will help keep plaque from building up.
- A professional cleaning by your dental professional is the only way to remove plaque that has built up and hardened into tartar. Your dental professional will clean or "scale" your teeth to remove the tartar above and below the gumline. If your condition is more severe, a root planing procedure may be performed. Root planing helps to smooth irregularities on the roots of the teeth making it more difficult for plaque to deposit there.
By scheduling regular check-ups, early stage gum disease can be treated before it leads to a much more serious condition. If your condition is more advanced, treatment will be required.
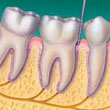 | Healthy Gums - Healthy gums are firm and do not bleed. They fit snugly around the teeth. | 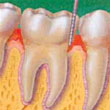 | Gingivitis - Gums are mildly inflamed, may appear red or swollen and may bleed during brushing. | |
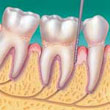 | Periodontitis - Gums begin to separate and recede from the teeth. This allows plaque to move toward the roots, supporting fibres and bone. | 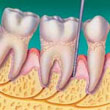 | Advanced Periodontitis - Supporting fibres and bone are destroyed. Teeth become loose and may need to be removed. |
This article is intended to promote understanding of and knowledge about general oral health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your dentist or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment.
Related Products

Helping dental professionals
More professionals across the world trust Colgate. Find resources, products, and information to give your patients a healthier future